
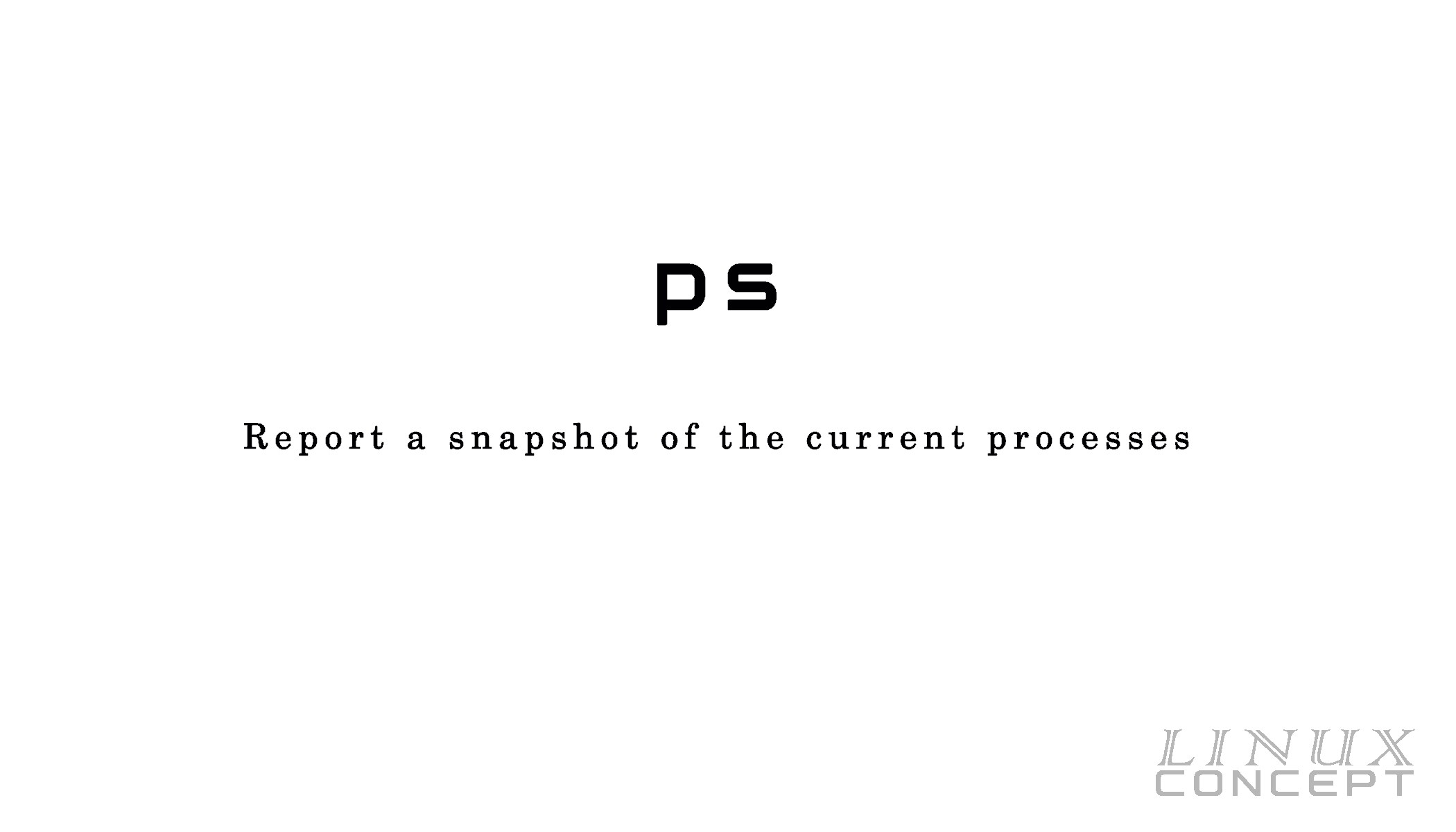
#Ps ef command in unix how to
Postfix 28780 1729 0 00:25 ? 00:00:00 pickup -l -t unix -u 5) How to Display a Specific Group Processes on Linux Using the ps Command # ps -fu dbus,ntp,postfixĭbus 1059 1 0 Mar16 ? 00:06:17 /usr/bin/dbus-daemon -system -address=systemd: -nofork -nopidfile -systemd-activation If you wish to display more than one UID process at a time, use the format below. If you need to display a specific user processes, use the following option with the ps command. Root 32263 1 0 19608 7804 0 Dec07 ? 00:00:38 /usr/local/apache/bin/httpd -k start -DSSL 4) How to Display a Specific User Processes on Linux Using the ps Command
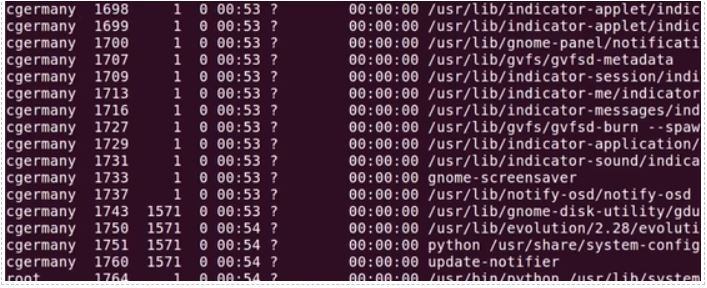
UID PID PPID C SZ RSS PSR STIME TTY TIME CMD If you want to get a detailed output (full format) use the following option.
#Ps ef command in unix full
Root 32263 0.0 0.0 78432 7804 ? Ss Dec07 0:38 /usr/local/apache/bin/httpd -k start -DSSL 3) How to List all Processes Running in the System in Full Format USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND # ps -eĪlternatively, you can use the following BSD style syntax. The following options show all user processes, which exclude processes associated with session leaders and terminals. It will show a snapshot of current processes running with detailed information of the process ID (pid=PID), the terminal associated with the process (tname=TTY), the cumulated CPU time in hh:mm:ss format (time=TIME), and the executable name (ucmd=CMD).ġ465 pts/0 00:00:00 ps 2) How to List all Processes Running in the System This is one of the most basic commands that shows the system running processes.
The ps command stands for process status.

In Linux, each process has a unique process ID (PID), which is automatically assigned to each process when it is created. What is process?Ī process is a command/running instance that is executed by a program or user. In this tutorial, we will show you how to find out the processes running on Linux using the ‘ps’ command. ‘ps’ and ‘top’ command are widely used by many Linux administrators to view running processes and discover which processes consume more resources in the system. Many Linux commands can be used to view processes running on a Linux system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
